As organizations evolve, so do their operational needs and the technologies available to meet them. Today’s enterprises are increasingly “automated”— relying on data, sensors, and AI-driven insights to create more efficient, adaptive, and innovative work environments.
Through the integration of data collection and automated systems, companies can streamline workflows, understand their resources better, and design workspaces that resonate with employees. But to achieve the full potential of the automated enterprise, leaders must not only implement the right technologies but also address the challenges that accompany automation.
Below, we’ll explore the benefits of an automated enterprise, the types of sensors and data collection involved, the role of data analytics and AI, and the challenges that enterprises must consider to thrive in this new era.
The benefits of the automated enterprise
Automation in the enterprise goes beyond simple process efficiency; it transforms the entire work ecosystem to create value on multiple fronts. The automated enterprise leverages data to drive more intelligent decision-making, improve resource management, and create a more adaptable, resilient business environment.
Using data to design a workplace your employees love
In establishing an automated enterprise, data is key to creating a workspace that prioritizes employee comfort, productivity, and engagement. By gathering and analyzing data on employee behavior, workplace usage, and feedback, enterprises can design spaces that resonate with the people using them every day.
For instance, sensor data on room occupancy, lighting preferences, and temperature variations can help adjust environments to employees’ real-time needs. This type of workplace design can have a direct impact on employee satisfaction, reducing turnover rates and fostering a culture that values employee well-being.
Understanding how employees move through and use different spaces can also help optimize layouts to support various work styles, whether collaborative, private, or remote. This data-driven approach to workspace design enables enterprises to adapt as employee needs change, ensuring a workplace experience that promotes both productivity and happiness.
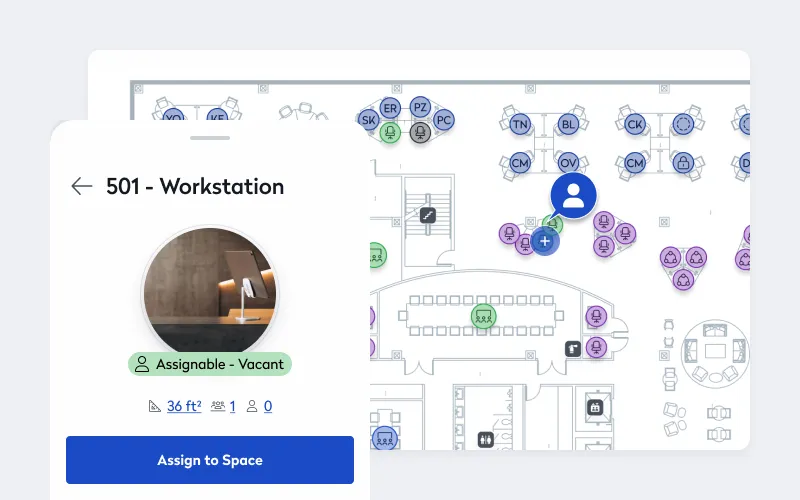
The automation of workspace management depends on an ecosystem of rich, continuously collected data that can provide actionable insights into how spaces are utilized. From usage patterns of meeting rooms to occupancy density in common areas, this data allows facilities managers to make informed adjustments. For example, real-time data on underutilized areas can help companies allocate resources more efficiently, reducing wasted space and optimizing usage across floors, departments, or even buildings.
Such insights not only lower operational costs but also align the physical environment with employee needs. Data-driven space optimization allows enterprises to support business growth while controlling overhead costs. Through strategic use of sensors and data analytics, enterprises can turn their physical spaces into agile assets that adapt to organizational needs.
Know your assets and their locations inside out
For any large enterprise, managing physical assets — ranging from desks and computers to specialized equipment — can be daunting. Automated asset tracking enabled by sensors and data analytics makes it easier to know exactly where assets are located, their condition, and whether they’re being optimally used. RFID tags, IoT sensors, and asset management software provide visibility into the status of essential resources, helping enterprises to maximize the value of each asset.
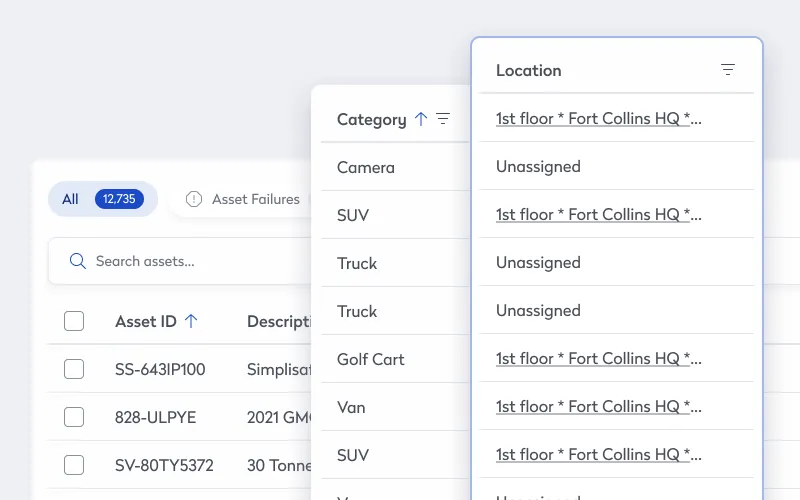
For example, sensors can alert managers when equipment needs maintenance, reducing unexpected downtime and improving the longevity of high-value items. They also help ensure critical assets are available where they’re needed most, eliminating time lost searching for misplaced equipment. This precise knowledge allows organizations to maximize the productivity and lifespan of their assets, ultimately saving costs and increasing operational resilience.
Data collection and types of sensors
Data collection in an automated enterprise relies on various types of sensors and data-gathering tools, each serving unique functions:
- Occupancy sensors: Track the presence of individuals in spaces to inform usage patterns and optimize layout.
- Environmental sensors: Monitor air quality, temperature, and humidity, ensuring the best conditions for employee comfort.
- Motion sensors: Detect movement to automate lighting, security, and climate control.
- RFID tags: Track assets and their movement, making it easier to locate and manage valuable equipment.
- Proximity sensors: Assist in space management and enable safe distancing protocols.
- Energy meters: Track energy usage, enabling organizations to manage power consumption and reduce costs.
- Cameras (with AI for privacy): Analyze space occupancy and movement trends without capturing identifiable information.
These sensors collectively enable data collection at scale, which feeds into analytics platforms and provides insights for strategic decision-making.
Data analytics and AI for an intelligent enterprise
Truly unlocking the potential of the automated enterprise means ensuring that data analytics and AI are front-and-center. They convert vast amounts of sensor and operational data into meaningful insights, empowering decision-makers with actionable intelligence. Here’s how data analytics and AI transform automation into tangible value:
- Predictive maintenance: Through AI-driven predictive analytics, enterprises can anticipate maintenance needs and address them before they result in costly breakdowns or downtime. Algorithms can detect signs of wear or irregular patterns, scheduling maintenance in advance and improving the reliability of essential assets.
- Operational efficiency: Data analytics identifies inefficiencies, allowing enterprises to streamline workflows. For example, machine learning algorithms can optimize supply chain processes by predicting demand surges and adjusting inventory levels, reducing waste and meeting customer needs more effectively.
- Enhanced security: AI-driven algorithms analyze real-time data from cameras, motion sensors, and access logs to identify potential security threats. The automated enterprise can respond faster to anomalies and use AI to develop proactive security protocols.
- Personalization of the workplace: Through data-driven insights, enterprises can create more personalized work environments that cater to individual employee preferences, such as lighting, temperature, or work style. This fosters a sense of inclusion and satisfaction that drives both productivity and morale.
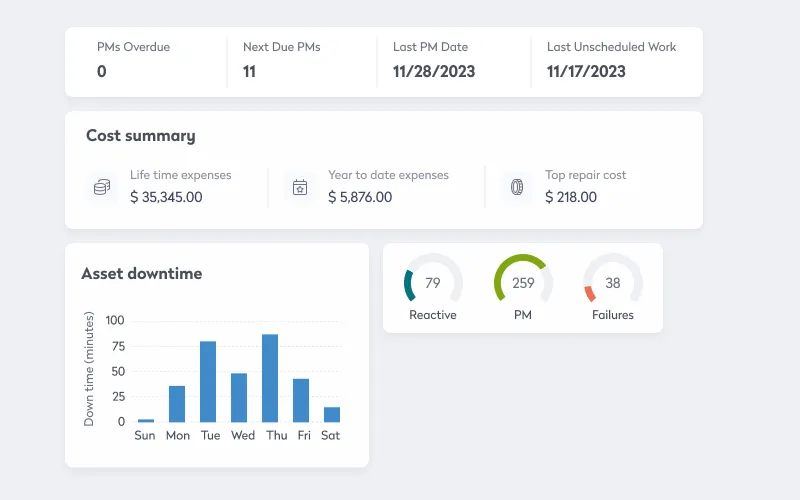
Data analytics and AI help enterprises pivot quickly, capitalizing on emerging trends and maintaining a competitive edge in a constantly changing market.
Challenges of enterprise automation
While the benefits of automation are clear, implementing and sustaining an automated enterprise comes with its own set of challenges. These hurdles require careful planning and strategic responses.
Data privacy and security
Data is essential to automation, but protecting that data is critical. When enterprises collect information on employee behavior, workspace usage, and asset location, they must handle it responsibly to protect privacy. Implementing robust security measures, anonymizing data, and ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR are essential steps in safeguarding data privacy.
Integration with legacy systems
Many enterprises rely on legacy systems that were not designed to support automation or data integration. Migrating from these systems to new, automated solutions can be complex, costly, and time-consuming. To mitigate this, enterprises can consider gradual integration strategies, ensuring compatibility with legacy infrastructure while moving toward fully automated processes.
Employee adaptation and change management
Automation can create concerns among employees about job security or increased oversight. Clear communication, transparency, and involvement of employees in the automation journey can help mitigate these concerns. Enterprises should provide training to help employees understand how automation supports their work, rather than replacing it, fostering a culture of empowerment and collaboration.
High implementation and maintenance costs
Implementing automation technologies, from AI analytics platforms to IoT sensors, requires significant investment. Furthermore, ongoing maintenance and upgrades add to the cost. Enterprises must perform a cost-benefit analysis to ensure the long-term value of automation outweighs initial expenses. By prioritizing automation initiatives that directly support business goals, companies can achieve a more favorable return on investment.
Build a business for the future with sophisticated automation tools
The automated enterprise represents the future of business operations, leveraging data, sensors, and AI to create a more adaptive and efficient work environment. By carefully implementing automation strategies and addressing challenges like data privacy, integration, and employee adaptation, organizations can maximize the benefits of automation. As enterprises continue to innovate and adopt new technologies, they can create workplaces that are not only more efficient but also more attuned to the needs of employees, ultimately driving long-term success and resilience.
Get in touch with Eptura about how workplace management software can help with your organization’s journey to full automation.








